what is the drop arm test|drop arm full thickness test : agent drop-arm test A possible rotator cuff tear can be evaluated with the drop-arm test. This test is performed by passively abducting the patient's shoulder, then observing as the patient. 20 horas atrás · The FIFA World Cup is expected to provide a gross domestic product benefit of about $392 million for Toronto and $456 million for Ontario. With files from The .
{plog:ftitle_list}
21 de fev. de 2024 · Today's fun fact: A single poison-arrow frog contains enough poison to kill over 2,000 people. Click for amazing games on your computer or mobile. Fireboy and Watergirl / Moto X3M / Pixel Force. Best Friv out there, always updated with new content.
The drop arm test is a physical examination test used by healthcare professionals to assess shoulder pain and potential rotator cuff injuries. It is typically . drop-arm test A possible rotator cuff tear can be evaluated with the drop-arm test. This test is performed by passively abducting the patient's shoulder, then observing as the patient. Enroll in our online course: http://bit.ly/PTMSK DOWNLOAD OUR APP:📱 iPhone/iPad: https://goo.gl/eUuF7w🤖 Android: https://goo.gl/3NKzJX GET OUR ASSESSMENT B.
The drop arm test is designed to determine a patient's ability to sustain humeral joint motion through eccentric contraction as the arm is taken through the full motion of abduction to .
The Drop Arm Sign or Drop Arm Test is a common orthopedic test to assess for full-thickness tears of the supraspinatus and infraspinatus. Drop Arm Test A rotator cuff tear will make it difficult for you to control your arm as it lowers, especially if any one of the 4 stabilizers of the rotator cuff are compromised. To .
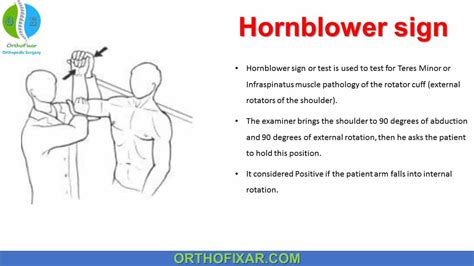
What it tests for: Rotator cuff injuries or limited range of motion. Positive result: Pain or limitation on the injured side compared to the uninjured side. Hornblower’s sign test. How it’s.
Codman's test is typically used in the assessment of a suspected rotator cuff tear. This test is also commonly referred to as the drop-arm test or sign.The Drop Arm test is used to help identify rotator cuff pathology, specifically supraspinatus and infraspinatus tears. To perform the Drop Arm test, position the patient in sitting or standing with the arm relaxed at their side. The .Purpose of Test: To test for the presence of a full-thickness rotator cuff tear. Test Position: Sitting or standing Performing the Test: The patient is told to actively elevate the arm in the scapular plane, followed by slowly reversing the .
Drop Arm Test is used to check for the integrity of the supraspinatus muscle of the rotator cuff of the shoulder. It’s sometimes called Codman’s test. The drop arm test determines the patient’s ability to control . This is a really great test for you to use with your patients who you suspect may have injured their Rotator Cuff, and in particular, may have suffered a Rot.The first is a drop test: the clinician drops the “paralyzed” arm over the patient's face. In pseudoneurologic syndrome, the “paralyzed” arm will not strike the patient's face when dropped .
Kathleen Carr, MD demonstrates the Drop Arm Test as part of a complete Shoulder Exam Drop Arm Test. A rotator cuff tear will make it difficult for you to control your arm as it lowers, especially if any one of the 4 stabilizers of the rotator cuff are compromised. To perform the drop arm test, simply raise your arm overhead in an arc, with as much range as possible. Now reverse the arc and lower your arm slowly, without assistance. When the drop arm test is used for a series of experiments like these, it could be more accurate: Empty or fully testable. Lag indicator for external rotation. Lag indicator for internal rotation. The Hornblower sign. To discriminate between rotator cuff muscles and provide a more reliable diagnosis, a battery of tests should be conducted.
Negative Test: The patient can smoothly and slowly lower the arm without difficulty, indicating the absence of significant rotator cuff pathology.; How the Drop Arm Test Helps in Diagnosing Rotator Cuff Tears? The drop arm test serves as a valuable screening tool for detecting rotator cuff tears, particularly involving the supraspinatus tendon.A positive test . Drop arm test: The patient’s shoulder is brought into a position of 90 degrees of shoulder abduction in the scapular plane. The examiner initially supports the limb and then instructs the patient to adduct the arm to the side of the body slowly. A positive test includes the patient’s inability to maintain the abducted position of the .
Drop-arm test: Active shoulder abduction to 90°, then return . Positive: Dropping the arm down with pain indicates a positive test; Drop Arm Test video provided by Clinically Relevant. Jobe/supraspinatus/empty can test: Resist shoulder abduction and internal rotation.Test Item Cluster: This test may be combined as a cluster with the Drop-Arm Sign and the Painful Arc Sign to test for the presence of a full-thickness rotator cuff tear. If all three tests report positive results, then the positive likelihood ratio is 15.6 and if all three tests are negative, the negative likelihood ratio is 0.16. Drop arm test is negative if the patient is able to control the lowering of the arm slowly and without pain. Drop arm test is positive if there is pain while lowering the arm, sudden dropping of the arm or weakness in maintaining arm position during lowering (with or without pain), suggesting injury to the supraspinatus 1 .Purpose [edit | edit source]. This is a shoulder special test which is meant to assess the integrity, and tears, of the supraspinatus (SSP) and infraspinatus muscles (muscles which collectively contribute to the rotator cuff complex). This test can also be used for the clinical examination of a shoulder impingement syndrome (SIS).. Another name for this test is the Infraspinatus Spring .
This Technique Peek video features Frank Hoeffner, DPT, OCS demonstrating how to perform drop arm test for the shoulder. This test is performed by passively .Purpose [edit | edit source]. The Empty Can Test, also known as the Jobe or Supraspinatus test, is used to assess for lesions of the rotator cuff, specifically the supraspinatus muscle and supraspinatus tendon.. Technique [edit | edit source]. The patients arm is actively abducted to 90 o; The examiner applies downward resistance to the abducted arm; With the patient's hand in . On the other hand, compared to the Hawkins test, we found a high value of LR negative ratio in the Jobe test, indicating poor diagnostic accuracy. However, LR values should be examined with caution as in the drop arm test. We found that the drop arm test had a high specificity and low sensitivity that provided a greater LR positive value.
The Drop-Arm Sign. Patient actively elevates the arm in the scapular plane and then slowly reverses the motion. A positive test is defined as the patient experiencing pain during the activity or that the arm suddenly drops. The Painful Arc Sign (Fig 1) Patient fully elevates the arm along the scapular plane and then slowly reverses the motion.Data in this study shows that if the drop arm test is positive one can almost be certain that the patient has a supraspinatus tear but a negative test does not provide conclusive information to the examiner. The drop arm test also cannot be used .Introduction [edit | edit source]. Traditionally Orthopaedic Special tests were used to assist in the diagnostic process by implicating specific tissue structures that are either dysfunctional, pathological, or lack structural integrity, confirming the findings from the physical assessment and providing a tentative diagnosis. Special testing is generally performed following a full .
A positive drop arm test increased the likelihood of rotator cuff disease (one study with 104 patients and 104 shoulders; positive likelihood ratio = 3.3; 95% CI, 1.0 to 11). Among the six pain .If all 3 are positive, there is a 98% chance of a rotator cuff tear; if 2 tests are positive and the patient is older than 60 years, the findings are suggestive of a tear; and if all 3 tests (plus the drop arm test) are negative, there is less than a 5% chance of a major rotator cuff tear.
Drop arm test. Pain with Jobe test. Infraspinatus. ER weakness at 0° abduction. ER lag sign. Teres minor. ER weakness at 90° abduction and 90° ER. Hornblowers. Subscapularis. IR weakness at 0° abduction. Excessive passive ER. Belly Press. Lift off. The drop arm sign is often used to diagnose a rotator cuff tear. The examiner brings the arm to 90 degrees of abduction and instructs the patient to maintai.This test is commonly used to identify possible subacromial impingement . arm shoulder in 90 degrees of shoulder flexion with the elbow flexed to 90 degrees and then internally rotates the arm. The test is considered to be positive if the patient experiences pain with internal rotation. This 20 minute video is a good overview of the shoulder .Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like drop arm test, patient is standing examiner is in front, arms falls uncontrollably from 90 degrees at the side or pain and more.
The drop arm test is negative, and there is no limitation with shoulder shrug. The patient is not holding his arm close to his side, and there is no tenderness to palpation in the bicipital groove when the arm is at the patient's side, flexed to 90 degrees, and then supinated against resistance.
positive hornblower's sign
positive drop arm sign
drop arm test shoulder positive
计算机. 子缀. 释义. 行业词典. 爱词霸权威在线词典,为您提供subfix的中文意思,subfix的用法讲解,subfix的读音,subfix的同义词,subfix的反义词,subfix的例句等英语服务。.
what is the drop arm test|drop arm full thickness test